When this tuna is cut into pieces, the meat is whitish, as if grilled in a fire, so it is called “Yake (焼け)” or “Yake-maguro (焼け鮪)” as “Yake” means “burnt” in this case. The meat can also be a grayish-brown. In the industry it’s known as “White tuna” due to its color. It loses its characteristic red color, the texture of the meat when eating it is flakey and it doesn’t taste good.
Even if the fish body is cooled with ice water after catching, once the meat has been “burnt”, it won’t turn back to red. This renders even the premium Pacific bluefin tuna and southern bluefin tuna worthless, with zero commercial value as food. However, the fishermen don’t just toss the dead fish back into the sea without a second thought. This is mostly processed into pet food. Also, since it can’t be determined externally whether the meat is “burnt” or not, no one can tell until the fish has been cut open. It runs a big risk to the broker and can be a cause of its fishing port brand losing credibility.
It is currently believed that burnt tuna occurs from high temperature and low pH in the muscles of the fish after death, and that there is a complicated, indirect causal relationship between the conditions such as the environmental temperature, fishing method, handling of the catch, length of processing time, type of fish and size of fish. However, the mechanism that causes this phenomenon is not clearly understood.
We hope this information will be helpful.
Revision date: March 1, 2022
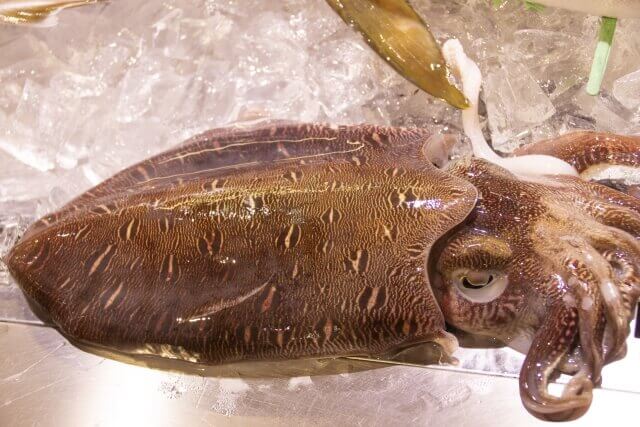
 No people in the world love squid more than the Japanese. Squid ranks third in import volume behind shrimp and tuna. Squid is brought to Japan from the oceans all over the world. There are between 400 and 500 species of wild squid on Earth. Some, like the pygmy cuttlefish, are tinier than 3 millimeters while the giant squid is over 10 meters.
No people in the world love squid more than the Japanese. Squid ranks third in import volume behind shrimp and tuna. Squid is brought to Japan from the oceans all over the world. There are between 400 and 500 species of wild squid on Earth. Some, like the pygmy cuttlefish, are tinier than 3 millimeters while the giant squid is over 10 meters.